For those experiencing hair loss, Propecia stands out as a sought-after remedy. This prescription medication, containing the active ingredient finasteride, effectively targets androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. Its ability to inhibit the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) significantly reduces hair thinning and promotes regrowth.
Before starting treatment, consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial. They can assess if Propecia is suitable based on individual health history and specific hair loss conditions. Typically, the recommended dosage is one 1 mg tablet taken daily. Consistency is key; noticeable results may take three to six months, so patience is essential.
While Propecia may help many, awareness of potential side effects is important. Some users report decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or mood changes. These side effects are not universal, but discussing any concerns with a physician ensures better management of treatment.
For best results, consider combining Propecia with other hair loss treatments, like minoxidil, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Proper nutrition and hair care routines can enhance the medication’s effectiveness and support overall scalp health.
- Prescription Propecia: A Practical Guide
- Dosage and Usage
- Potential Side Effects
- Understanding the Active Ingredient in Propecia
- Indications for Use: Who Should Consider Propecia?
- Dosage Recommendations for Effective Results
- Timing and Administration
- What to Expect
- Potential Side Effects and Risk Factors
- Comparing Propecia with Other Hair Loss Treatments
- Consultation Process: What to Expect from Your Doctor
Prescription Propecia: A Practical Guide
Consult a healthcare professional before starting Propecia to determine if it’s suitable for your hair loss condition. This medication primarily treats male pattern baldness and is known to block DHT; a hormone linked to hair loss.
Dosage and Usage
Propecia is typically prescribed in a dosage of 1 mg taken once daily. Consistency is key; take it at the same time each day to establish a routine. Swallow the tablet whole, without crushing or chewing, to maintain its efficacy.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, Propecia may cause side effects. Some individuals experience decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or ejaculation disorders. These effects often resolve after discontinuation of the medication, but consult your doctor if they persist or if you experience any unusual symptoms.
| Side Effect | Occurrence | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Decreased libido | Common | Consult a doctor |
| Erectile dysfunction | Less common | Consult a doctor |
| Breast tenderness | Rare | Seek medical attention |
Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are important to monitor progress and address any concerns. Positive results may take several months, so patience is essential as you assess treatment effectiveness.
Understanding the Active Ingredient in Propecia
The active ingredient in Propecia is finasteride, a medication primarily used to treat male pattern baldness and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By reducing DHT levels, finasteride helps prevent hair loss and promotes hair regrowth in individuals experiencing androgenetic alopecia.
Adhere to your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding dosage and duration of therapy. Some users may experience side effects, including sexual dysfunction or mood changes. Discuss any concerns with your doctor, as they can provide guidance tailored to your specific health needs.
Overall, understanding finasteride’s role in Propecia allows users to manage expectations and commit to the treatment plan effectively. Tracking progress through photos or consultations can help gauge the efficacy of the medication over time.
Indications for Use: Who Should Consider Propecia?
Men experiencing androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness, should consider Propecia. This condition typically begins in the late teens to early twenties and progressively worsens over time. Propecia is specifically indicated for males seeking to slow hair loss and promote regrowth.
Individuals who notice thinning hair on the crown or a receding hairline can benefit from Propecia. It works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone primarily responsible for hair loss in this condition. By intervening in this hormonal process, Propecia can lead to visible improvements.
Those with a family history of hair loss may also find Propecia advantageous. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in hair loss, and early treatment may yield better results in maintaining existing hair and stimulating new growth.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate if Propecia is suitable. Discuss any existing medical conditions and medications, as these factors may influence the decision. Regular follow-ups will aid in monitoring progress and addressing any side effects.
In summary, men facing pattern baldness should evaluate Propecia as a viable option, especially if it’s in the early stages or there’s a familial tendency for hair loss. Regular consultation with a healthcare professional ensures safe and effective use.
Dosage Recommendations for Effective Results
The standard dosage for Propecia (finasteride) is 1 mg taken once daily. Taking this dose consistently ensures that the medication maintains its efficacy in preventing hair loss and promoting regrowth in men experiencing androgenetic alopecia. It’s important to adhere to this daily routine for optimal results.
Timing and Administration
Take Propecia at the same time each day to develop a habit. It can be taken with or without food, which adds flexibility to your routine. Swallow the tablet whole, and avoid crushing or chewing it to maintain its integrity. Consistency will help track your progress more effectively.
What to Expect
Visible results usually appear after three to six months of daily use. Monitor your hair growth and loss during this period. If you do not notice any improvement after 12 months, consult your healthcare provider to discuss ongoing treatment options.
Potential Side Effects and Risk Factors
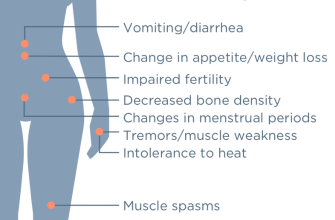
Propecia, while effective, may cause side effects that vary in severity. Users often report decreased libido and erectile dysfunction. These effects can lead to emotional distress, so discussing concerns with a healthcare provider is crucial.
Other potential side effects include breast tenderness, gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue in men), and skin rash. Although these reactions are less common, they can occur. Any noticeable changes in your body or mood should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare professional.
Individuals with liver issues should approach Propecia with caution, as the medication is metabolized in the liver. Pre-existing hormonal imbalances might also heighten the risk of adverse effects. Regular monitoring and open communication with a doctor can help mitigate potential risks.
Research indicates a potential link between Propecia and depression, anxiety, or suicidal thoughts in rare cases. Awareness and vigilance regarding mental health when starting this medication can be beneficial. If any symptoms arise, seek guidance without delay.
Women, especially those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, should avoid Propecia, as it can cause significant harm to a developing fetus. Always inform your healthcare provider of any existing conditions or medications before beginning treatment.
In summary, being informed about the side effects and risk factors associated with Propecia can empower users to make educated decisions. Maintaining an ongoing dialogue with healthcare professionals will ensure safe use and address any concerns efficiently.
Comparing Propecia with Other Hair Loss Treatments
Propecia (finasteride) stands out among hair loss treatments due to its specific action on dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a key factor in androgenetic alopecia. When considering alternatives, it’s crucial to evaluate their mechanisms, efficacy, and side effects.
Here are some popular hair loss treatments compared with Propecia:
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
- Topical application stimulates hair follicles directly.
- Available over-the-counter in liquid or foam forms.
- Can be used by both men and women; however, results take longer to appear compared to Propecia.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery
- Involves relocating hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another.
- Permanent solution with immediate results, but requires significant recovery time.
- Costly compared to Propecia and may not be suitable for all candidates.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Painless procedure using lasers to promote hair growth.
- Generally safe with minimal side effects; results may vary widely among users.
- Less researched than Propecia, and effectiveness can be inconsistent.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Involves injecting concentrated platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- Some studies show positive outcomes, but more research is needed.
- Can be expensive, and multiple sessions may be required for optimal effect.
Choosing between Propecia and other treatments depends on individual needs and condition severity. Propecia effectively halts hair loss for many men, while topical options like Minoxidil offer a less invasive alternative. Surgical options provide a permanent answer, yet they demand significant time and investment. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course for your specific situation.
Consultation Process: What to Expect from Your Doctor
Your doctor will begin the consultation by asking about your medical history and any medications you currently take. Be prepared to provide detailed information about your hair loss, including when it started and any previous treatments you have attempted.
Next, your doctor will likely perform a physical examination of your scalp to assess the extent of hair loss. This may include checking for any underlying scalp conditions that could be contributing to hair thinning or loss.
During your visit, expect your doctor to discuss the effectiveness and potential side effects of Propecia. They will explain how the medication works to inhibit hair loss and promote regrowth. Questions regarding your expectations and concerns are welcomed, so voice any uncertainties you may have.
If suitable for you, your doctor may prescribe Propecia and provide guidance on how to take the medication. The typical dosage is one tablet daily, and adherence to the prescribed regimen will optimize results. Additionally, they may offer advice on lifestyle changes that can enhance hair health.
Your doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment to monitor your progress, usually within a few months. At this visit, they will evaluate the results of the treatment and adjust your plan if needed.
Open communication with your doctor throughout this process is crucial. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or express any side effects you experience while on Propecia. Regular check-ins will help ensure that your treatment plan remains effective and tailored to your needs.