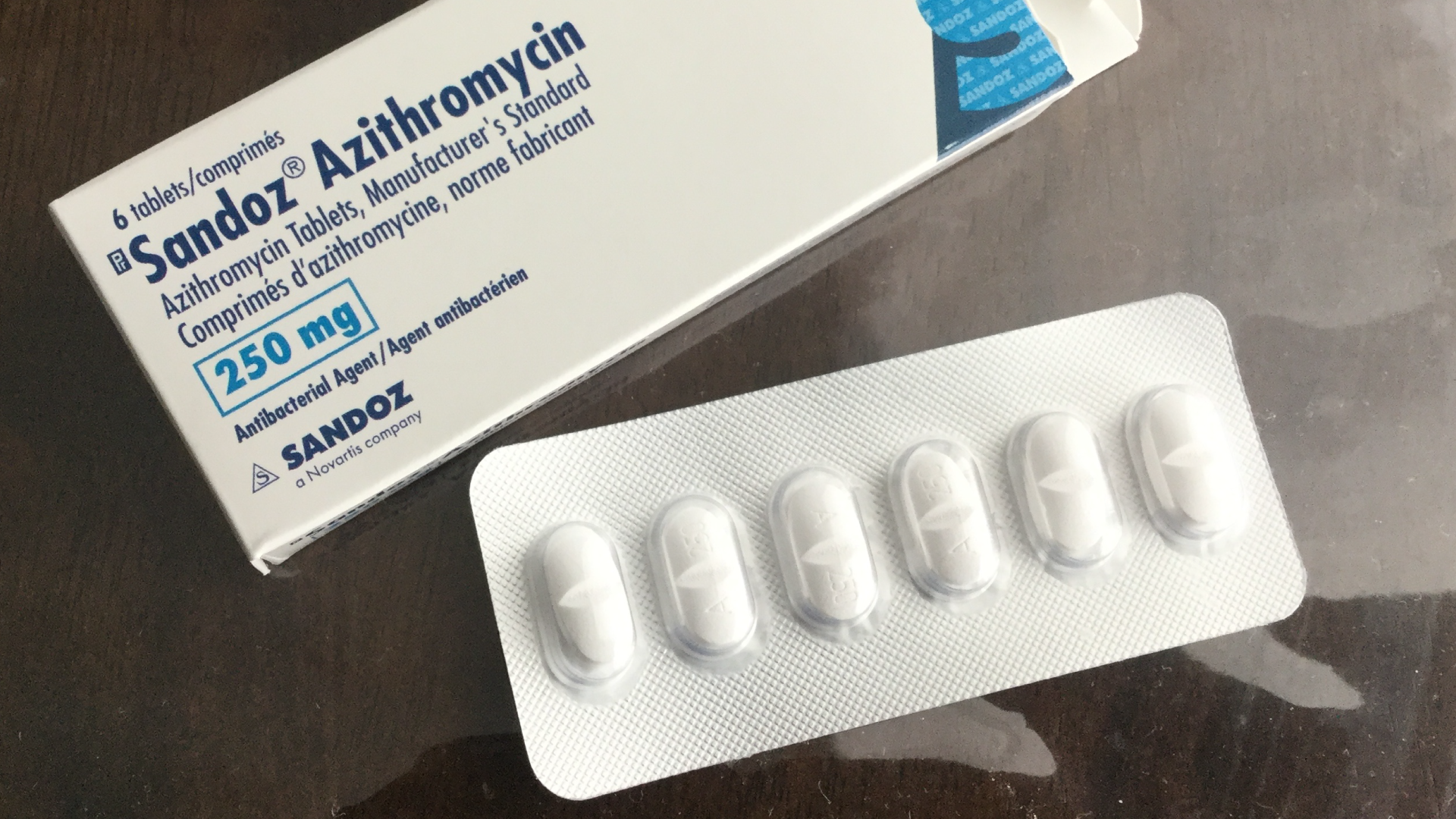
When dealing with bacterial infections, Zithromax (azithromycin) often serves as a go-to prescription drug. This antibiotic effectively combats a variety of conditions, including respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. If your healthcare provider identifies a bacterial infection, they may recommend Zithromax for its efficacy and relatively simple dosing regimen.
Taking Zithromax typically involves a three to five-day course, depending on the type and severity of the infection. Unlike some antibiotics that require frequent dosing throughout the day, Zithromax is designed to be taken once daily, which enhances adherence to the treatment plan. This convenience can help ensure that patients complete the full course, essential for maximizing the drug’s effectiveness and minimizing the risk of resistance.
Side effects may occur, though many people tolerate the medication well. Common reactions include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea or diarrhea. Always discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider, who can offer personalized guidance based on your medical history and current medications. Being informed about what to expect helps you manage any reactions swiftly, ensuring a smoother treatment experience.
As with any medication, it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely when using Zithromax. The antibiotic’s effectiveness relies on its proper use, including completing the full course even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This adherence not only aids your recovery but also contributes to broader public health efforts by preventing antibiotic resistance.
- Zithromax Prescription Drug: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Zithromax: Uses and Indications
- Common Uses of Zithromax
- Indications for Prescription
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Methods for Zithromax
- Administration Methods
- Special Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Zithromax
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
Zithromax Prescription Drug: A Comprehensive Guide
Zithromax, known generically as azithromycin, is an antibiotic that fights bacteria in the body. It’s commonly prescribed to treat various infections, including respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Dosage typically depends on the infection type and patient’s medical history. For adults, a common regimen starts with 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg once daily for four additional days.
Taking Zithromax is straightforward. It’s available in tablet, suspension, and injectable forms. Administer with or without food; however, taking it with food may help reduce potential stomach upset. Ensure to complete the full prescribed course, even if symptoms improve early.
Like all medications, Zithromax can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain, and headaches. Rare but serious side effects may occur, such as severe allergic reactions or heart rhythm changes. Consult a healthcare professional if unusual symptoms arise.
Before starting treatment, inform your doctor of any existing medical conditions, particularly liver or kidney disease, and any other medications being taken. Zithromax can interact with certain drugs, potentially leading to complications.
For patients with specific conditions, such as myasthenia gravis, caution is advised. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider prior to use.
Obtaining a prescription for Zithromax involves a consultation with a healthcare professional. Discuss your symptoms and receive the appropriate guidance tailored to your needs. Ensure follow-up as required to monitor progress.
When stored, keep Zithromax in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Discard expired or unused medication responsibly, following local regulations.
Understanding Zithromax: Uses and Indications
Zithromax, also known as azithromycin, serves as an antibiotic that targets various bacterial infections. It primarily treats respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis, as well as ear infections and throat infections. Additionally, Zithromax is effective against certain sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, making it a versatile choice for healthcare providers.
Common Uses of Zithromax
This medication plays a significant role in managing conditions like sinusitis, skin infections, and some types of gastrointestinal infections. Its broad-spectrum activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria allows it to be prescribed when patients exhibit resistance to other antibiotics.
Indications for Prescription
Healthcare professionals often prescribe Zithromax for patients with allergies to penicillin or those experiencing complications from respiratory tract infections. Additionally, it is indicated for those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are prone to bacterial exacerbations. Understanding when to use Zithromax can enhance recovery outcomes for various infections while minimizing antibiotic resistance risks.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Methods for Zithromax
For adults, Zithromax (azithromycin) is typically prescribed as a loading dose of 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg once daily for the next four days. This results in a total of 1,500 mg over the five-day period. For children, the dose is calculated based on weight, generally at 10 mg/kg on day one, followed by 5 mg/kg for the following four days, with a maximum dose of 500 mg per day.
Administration Methods
Take Zithromax with or without food. Consistency is key; choose either method and stick with it throughout the course of treatment. If you experience gastrointestinal discomfort, taking it with food may help alleviate symptoms. Swallow the tablets whole; do not crush or chew them. Liquid formulations should be shaken well before taking to ensure even distribution of the medication.
Special Considerations
Patients with impaired liver function may require dosage adjustments. Always inform your healthcare provider of any existing health issues or medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions. For those with renal impairment, no adjustment is necessary for insulin or patients on hemodialysis, but monitoring is still recommended. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as possible unless it’s almost time for the next dose. Do not double up.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions precisely, and complete the entire course of treatment to prevent antibiotic resistance. If symptoms persist or worsen, contact your healthcare provider promptly for further evaluation.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Zithromax
Patients taking Zithromax (azithromycin) should be informed about potential side effects and drug interactions to ensure safe usage.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Rash
If any of these symptoms become severe or persistent, seek medical attention immediately.
Serious Side Effects
- Severe allergic reactions (e.g., itching, swelling, trouble breathing)
- Liver problems (e.g., jaundice, dark urine, pale stool)
- Heart rhythm changes (e.g., palpitations, fainting)
- Severe intestinal condition (e.g., Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea)
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any serious side effects.
Drug Interactions
Be aware of possible interactions with the following medications:
- Antacids: May decrease absorption; take at least 2 hours apart.
- Coumadin (warfarin): Increased risk of bleeding; monitor INR closely.
- Digoxin: May increase digoxin levels; check for symptoms of toxicity.
- Other antibiotics: Interactions can reduce effectiveness.
Always discuss all medications, including over-the-counter and herbal products, with your healthcare provider to avoid adverse interactions.